Last Update: October 11, 2024
BY eric
eric
Keywords
Installation of Linux distro has became easy for a very long time, but still sometimes weird thing happens you might not know what goes wrong and get frustrated. I have installed Linux on Dell, HP computers and never had any issue. But when I installed Ubuntu on a Lenovo laptop, a ThinkPad, it wouldn't boot up after the installation. I tried to reinstall it, but it didn't work. I tried to repair the GRUB (sudo grub-install --root-directory=/mnt/boot), but again still no luck. It seemed like the computer couldn't find any bootable records on the drive.
After a quick search on the Internet, it seems I am not alone. The issue might be related to the TPM (Trusted Platform Module) enabled in the BIOS. People were suggesting to disable the TPM in the BIOS, and it should work. I went to the BIOS, disabled the TPM, and voila, it worked (another installation or GRUB fix is needed). The Ubuntu booted up without any issue.
Below are the steps to disable the TPM in the BIOS:
- To get into BIOS, restart the computer and press the
F1key when the Lenovo logo appears on the screen.
On the screen you may see "if you want to interrupt normal startup, press enter" or "to enter setup, press F1". Press F1 to enter the BIOS.
- Go to the
Securitytab.
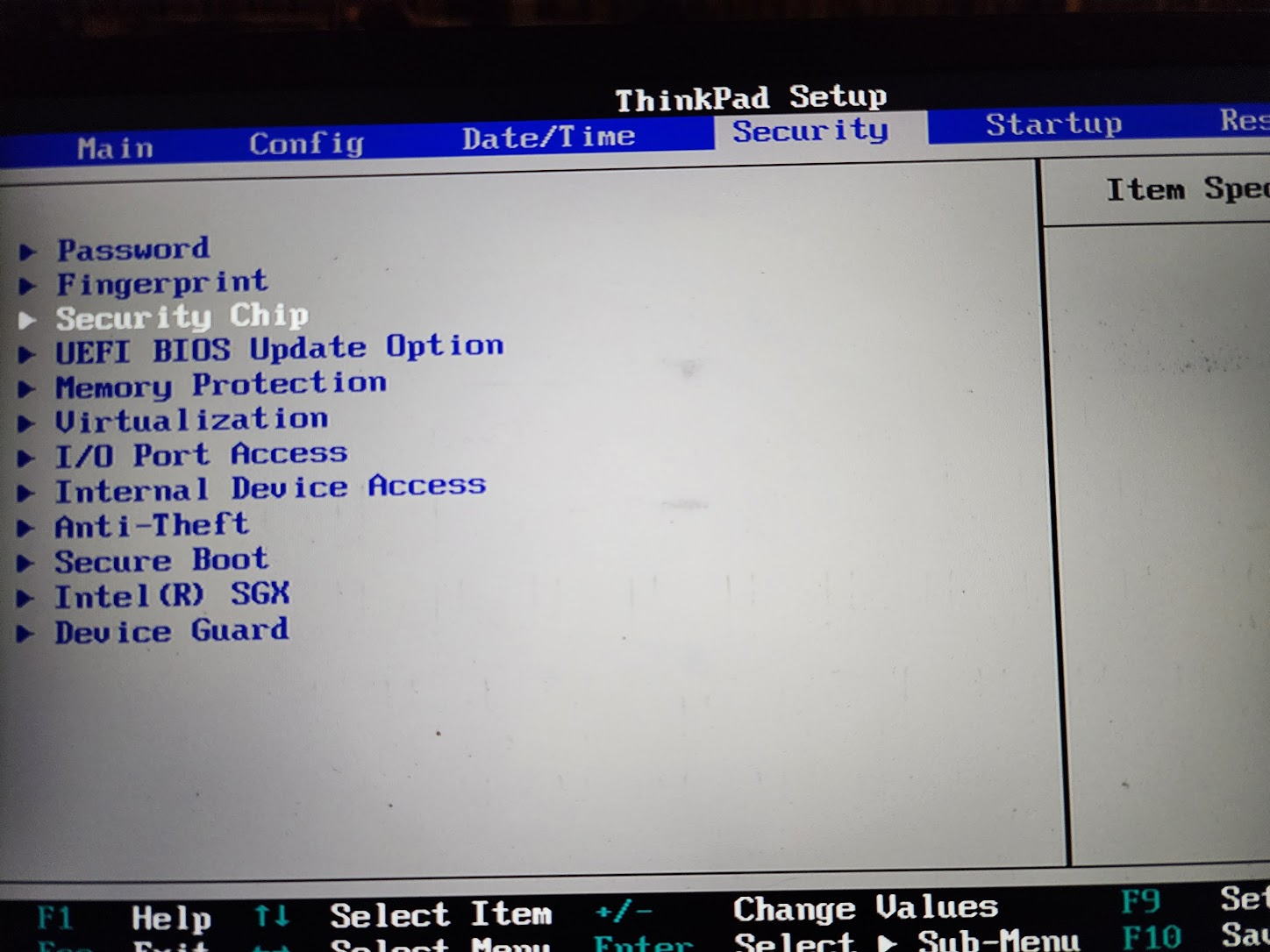
- Go to the
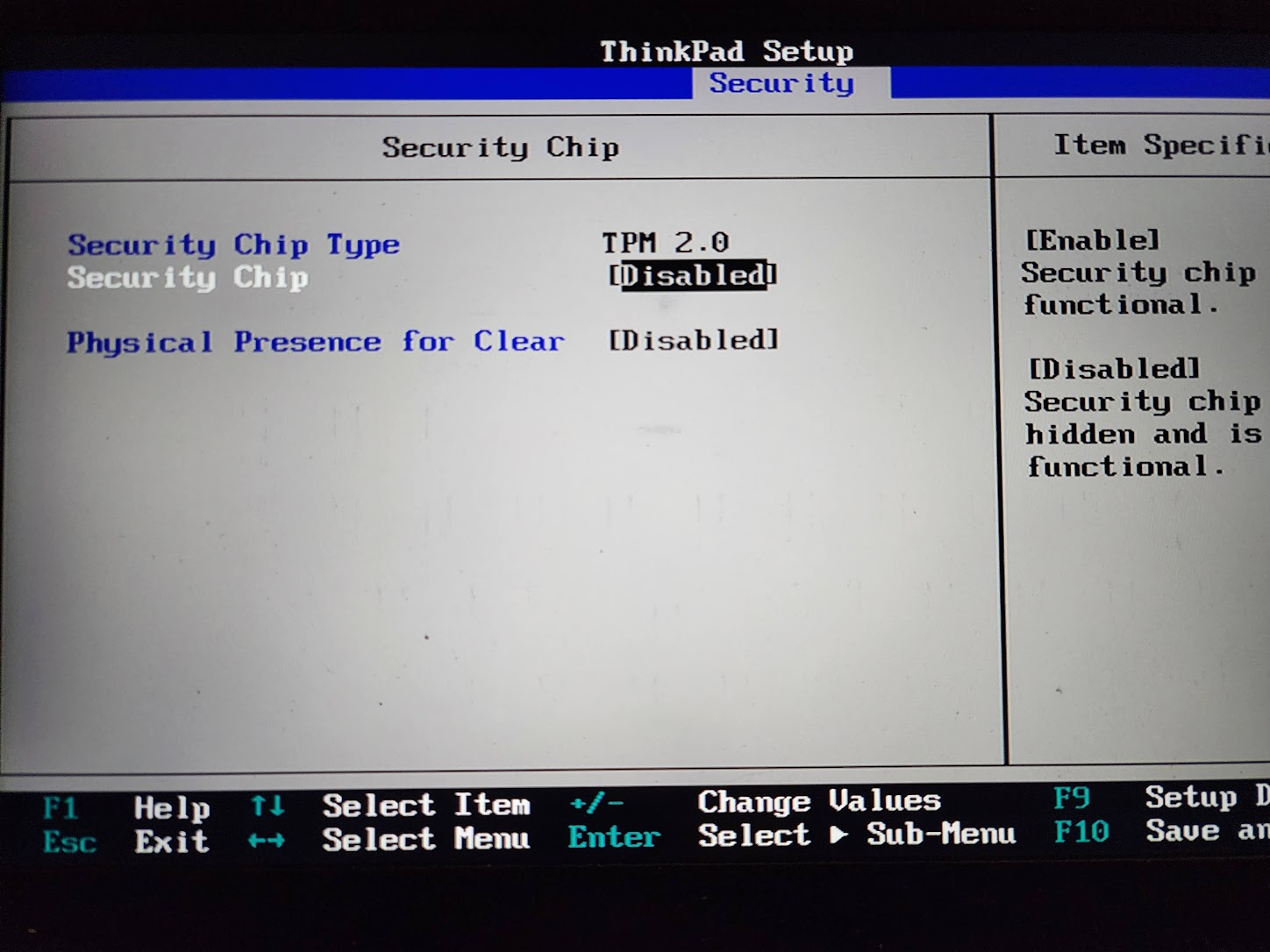
Security Chipoption.
Hit Enter.
- Change the value to
Disabled.
- Press
F10to save and exit.
In some cases, you probably need to disable secure boot as well.
So, if you have difficulty in getting Ubuntu (or any other distros, Fedora, CentOS, etc.) to boot after the installation, try to disable the TPM in the BIOS. It might work for you too, but with probably another installation.
Further Reading
According to Intel, the TPM is a hardware-based security feature that can help protect your computer by integrating cryptographic keys into devices. If your computer has the 8th Generation or later Intel processor, mostly you will have the security option in the BIOS of your computer. When it is enabled, the bootloader either cannot not be changed by the Ubuntu installer even Ubuntu supports UEFI Secure Boot, or the key provided by the TPM is ignored or not handled by Ubuntu, so it cannot proceed to boot up.
For Windows users, in order to run Windows 11, TPM 2.0 is required. So, if you disable the TPM, you might not be able to run Windows 11. But for Linux users, it should be fine.
Credits:
Photo by Arthur Mazi on Unsplash
Previous Article
Nov 28, 2024
Fixing Poor VOIP Sound Quality and Call Crackling
Fixing Poor VOIP Sound Quality and Call Crackling. Through analyzing the issue and providing a solution for fixing poor VOIP sound quality and call crackling.
Next Article
Jun 28, 2024
A Comparison of Different Types of MetaTrading Libraries for Algorithmic Trading
A Comparison of Different Types of MetaTrading Libraries for Algorithmic Trading.